Lifestyle
Why women need to get a pap smear
Taking care of your health is incredibly important, and one of the best ways to do that is through preventive screenings.
What is a Pap smear?
A Pap smear, also known as a Pap test, involves collecting cells from your cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus.
This test is designed to identify any abnormal cells that might develop into cervical cancer. It’s a straightforward and quick procedure, usually done during a routine pelvic exam.
Detecting cervical cancer early
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women worldwide. However, it is highly treatable when caught early. The Pap smear can identify precancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix before symptoms appear. Early detection means treatment can begin promptly, significantly improving the chances of a successful outcome.
Identifying Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to cervical cancer. Not all HPV infections cause cancer, but certain high-risk types can significantly increase the risk.
A Pap smear can detect the presence of HPV, allowing for further monitoring and treatment if necessary. By catching HPV early, doctors can develop a plan to manage the infection and reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Monitoring changes in cervical health
Regular Pap smears help monitor changes in the cervix over time. By comparing results from different tests, doctors can identify any patterns or abnormalities that need closer attention. This ongoing monitoring allows for a proactive approach to health care, catching potential issues before they become serious problems.
One of the most valuable aspects of regular Pap smears is the peace of mind they offer. Knowing that you are taking steps to monitor and protect your health can alleviate anxiety and stress.
The procedure is quick and generally painless, and the reassurance it provides far outweighs any temporary discomfort.
Who needs a Pap smear?
Most women should start getting Pap smears at age 21 and continue every three years. Women over 30 may combine the Pap test with an HPV test and extend the screening interval to every five years if both results are normal. However, women with certain risk factors, such as a history of cervical cancer or a weakened immune system, may need more frequent screenings. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best screening schedule for you.
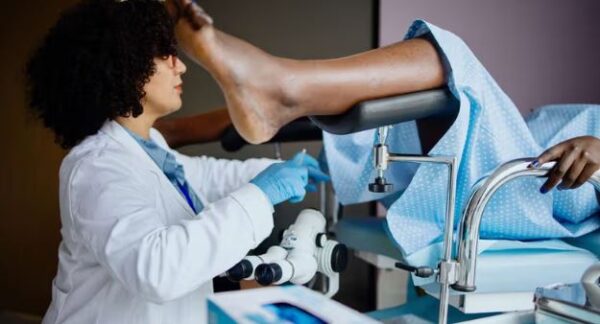
What to expect during a Pap smear
Understanding what happens during a Pap smear can help reduce any anxiety. During the test, you will lie on an exam table with your feet in stirrups.
The doctor will insert a speculum into your vagina to widen it and gain access to the cervix. Using a small brush or spatula, they will gently collect cells from the cervix. The sample is then sent to a lab for analysis. The entire procedure takes only a few minutes.
After the Pap smear
After the test, you might experience mild discomfort or spotting, but these symptoms usually pass quickly. If your results are normal, you will continue with your regular screening schedule. If the results are abnormal, it doesn’t necessarily mean you have cancer. It means further testing is needed to understand the cause of the abnormal cells.
Regular Pap smears are a vital part of women’s health care, helping to detect cervical cancer and other issues early. By scheduling a Pap smear every three years, you take an important step in protecting your health and ensuring a brighter, healthier future.
Don’t let fear or uncertainty hold you back—talk to your doctor today about scheduling your next Pap smear. Your health is worth it.