Cruciferous vegetables contain compounds like phytonutrients and glucosinolates that have been shown to have anticancer effects.
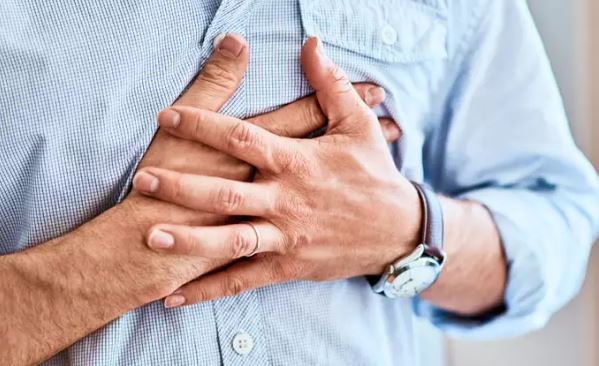
A new study has also linked higher consumption of cruciferous vegetables with less extensive blood vessel disease such as heart attack or stroke in older women.
Heart attack or stroke may be caused due to the build-up of fatty and calcium deposits on the inner walls of our blood vessels, such as the aorta.
Researchers suggested that vitamin K, which is found abundantly in cruciferous vegetables, may be involved in inhibiting the calcification process that occurs in our blood vessels.
With that being said, here are top five cruciferous vegetables that should be added to your daily diet:
1. Broccoli
Consuming steamed broccoli regularly may help cut risk of cardiovascular disease by reducing cholesterol in the body – suggested a study by Nutrition Research. It could also help reduce the risk of heart disease, build strong bones, improve eye health, and prevent cancer.
2. Cauliflower vegee
When you consume 100 grams of cauliflower, 92 grams are actually water. Thus, eating this veggie can help keep you hydrated. Cauliflower also has anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antibacterial effects.
3. Cabbage leaves
Cabbage, especially red cabbage, is good for your heart. This vegetable can raise levels of beta-carotene, lutein, and other heart-protective antioxidants and lower “oxidized” LDL, which is linked to hardening of the arteries. Cabbage also has anti-inflammatory effects, which can help prevent heart disease.
4. Brussel sprouts
Including more of these nutritionally dense vegetables in your diet could provide significant health benefits, such as improving bone health, managing diabetes, decreasing the risk of heart disease and some cancers.
5. Kale
Eating kale can help lower cholesterol, which may reduce your risk of heart disease. Kale is one of the world’s best sources of vitamin K, an important nutrient that is involved in blood clotting. This cruciferous vegetable also contains numerous substances that have been shown to help fight cancer in test-tube and animal studies.